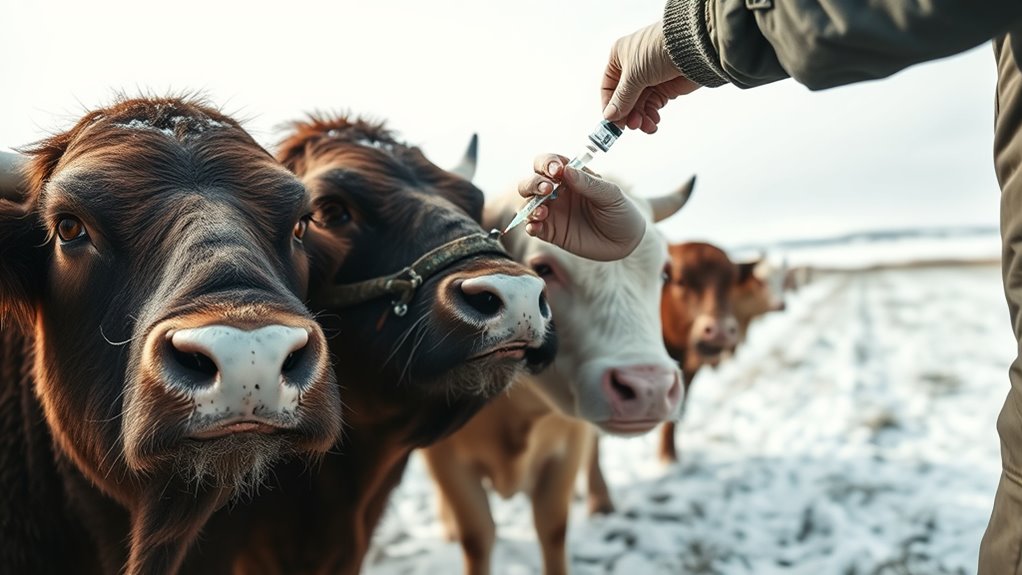
Vaccinating your livestock ahead of winter is vital to protect them from cold-weather diseases and reduce stress on their immune systems. Start vaccines 4 to 6 weeks before cold weather hits to give animals enough time to build immunity. Choose the right vaccines for common winter threats like pneumonia, parasites, and bacterial infections. Proper preparation, handling, and keeping accurate records ensure you stay on track. Keep going to learn more about effective vaccination strategies and tips.
Key Takeaways
- Vaccinate at least 2-4 weeks before cold weather to allow immunity development prior to winter exposure.
- Select appropriate vaccines targeting regional diseases, considering age, breed, and specific risks.
- Prepare animals by ensuring good health, proper nutrition, and minimal stress for optimal vaccine response.
- Use sterile techniques and proper handling to ensure effective vaccination and prevent infections.
- Maintain detailed vaccination records to monitor schedules, boosters, and herd immunity status.
Understanding the Importance of Winter Vaccination
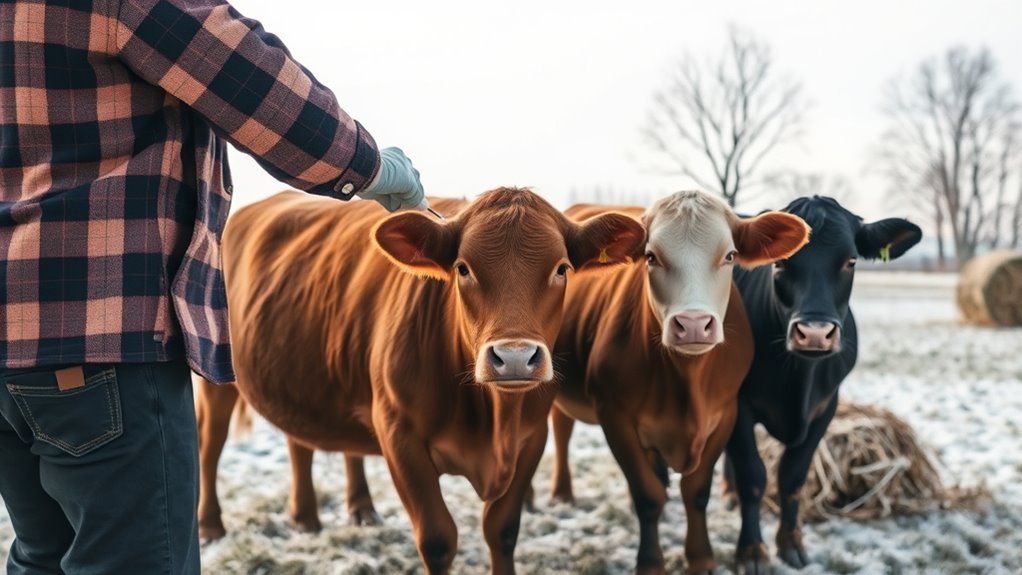

Winter creates ideal conditions for many livestock diseases to spread, making it essential to vaccinate your animals ahead of the season. Cold weather and reduced ventilation in shelters can increase disease transmission among your livestock. When animals are stressed from the cold, their immune systems weaken, making them more vulnerable to infections. Vaccinating before winter helps build immunity early, reducing the risk of outbreaks during this vulnerable period. It also ensures your livestock stay healthy, maintain proper weight, and continue productive routines like milk production or growth. Skipping vaccination can lead to severe health issues that are harder to control once the season starts. Taking proactive steps now safeguards your animals’ health and minimizes winter-related losses. Additionally, understanding the veterinary vaccination schedule can help optimize protection.
Timing Your Vaccination Schedule for Optimal Protection
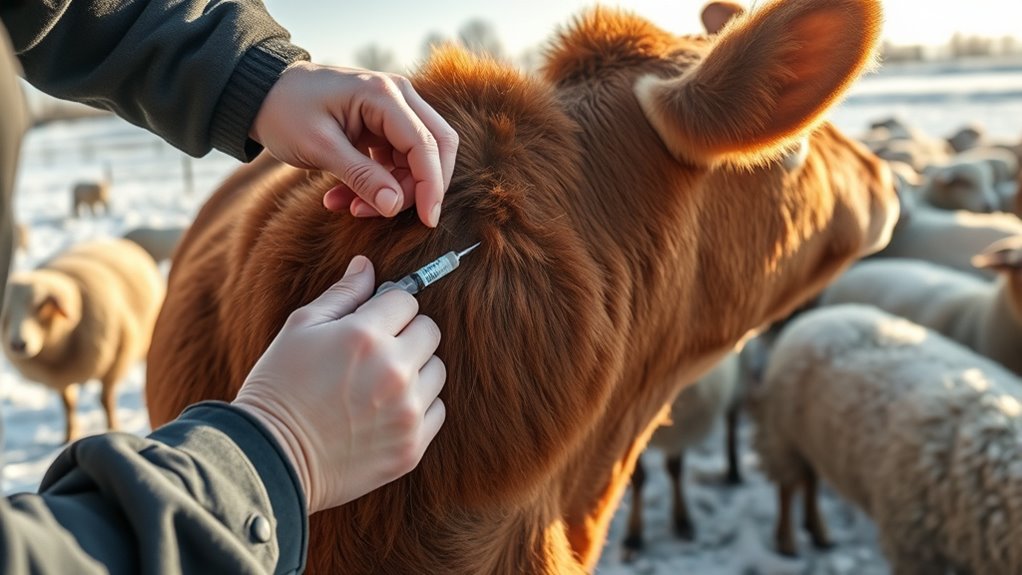

Planning your vaccination schedule carefully guarantees your livestock are protected when they need it most. To do this effectively, you must consider vaccine timing relative to disease exposure and immune response development. Typically, administer vaccines at least 2-4 weeks before cold weather arrives, allowing immunity to build. Keep in mind that different vaccines have varying intervals; some require booster shots. Use the table below to understand key timing factors:
| Factor | Recommended Timing |
|---|---|
| Primary vaccination | 4-6 weeks before winter |
| Booster shots | 2-3 weeks after primary |
| Cold weather onset | Plan vaccinations 4 weeks prior |
| Immune response window | 2-3 weeks post-vaccination |
| Disease exposure risk | Schedule before high-risk periods |
Getting timing right ensures your livestock are shielded when they face the highest risks. Additionally, staying informed about AI in Education developments can help improve training and knowledge dissemination for livestock vaccination strategies.
Common Diseases to Prevent Before Winter Sets In

As temperatures drop and animals spend more time indoors, preventing common diseases becomes critical for livestock health. Respiratory illnesses like pneumonia and infectious bovine rhinotracheitis can spread rapidly in crowded conditions, so make certain your animals are vaccinated against these. Parasites such as worms and lice thrive in winter, weakening your livestock’s immune system and increasing their susceptibility to other diseases. Clostridial diseases, including tetanus and blackleg, pose a significant threat if wounds occur or if bacteria are present in contaminated feed or soil. Additionally, contagious diseases like foot-and-mouth and bovine viral diarrhea can cause severe outbreaks during winter months. By vaccinating your animals against these common threats, you help maintain herd health, reduce mortality risks, and ensure your livestock are prepared for the harsher months ahead. Regular health monitoring and disease prevention strategies further enhance your herd’s resilience during the colder seasons.
Selecting the Right Vaccines for Your Livestock
Choosing the right vaccines for your livestock is essential to effectively prevent disease and protect herd health. You need to contemplate factors like age, breed, and local disease risks. Consult with your veterinarian to identify which vaccines target prevalent illnesses in your area. Not all vaccines suit every farm, so selecting the right ones ensures ideal immunity without unnecessary costs.
| Vaccine Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Live | Stimulates strong immunity |
| Killed | Safer, for vulnerable animals |
| Factors to Contemplate | Why It Matters |
| Age of animals | Different age groups require tailored vaccines |
| Disease prevalence | Focus on common threats in your region |
Preparing Your Animals for Vaccination
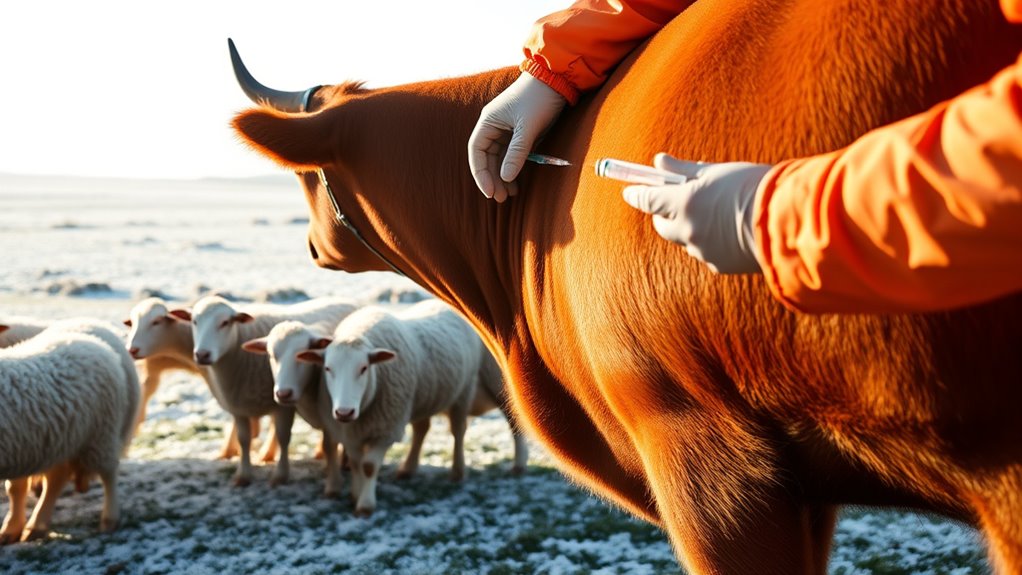

Before vaccinating, you need to check your animals’ health status to guarantee they’re fit for the shot. Make sure they’re properly nourished, as good nutrition helps them respond better to vaccines. Also, schedule the vaccination at the right time to maximize effectiveness and minimize stress. Maintaining privacy and boundaries can help reduce stress during vaccination procedures and ensure your animals remain calm.
Check Animal Health Status
Have you checked your animals’ health before vaccination? It’s crucial to evaluate their overall condition to make certain they’re fit for the process. Look for signs of illness, such as lethargy, loss of appetite, nasal discharge, or coughing. Animals that are sick or stressed may not respond well to vaccines and could develop complications. Conduct a quick physical exam, checking for abnormal temperatures or swelling. If you notice any health issues, consider postponing vaccination until they recover. Ensuring your livestock are healthy minimizes risks and maximizes vaccine effectiveness. Recognizing signs of fatigue or stress can help determine if animals are ready for vaccination. Remember, a healthy animal is more likely to develop proper immunity. Taking these steps now helps protect your herd and ensures a smoother vaccination process ahead of winter.
Ensure Proper Nutrition
Ensuring proper nutrition is essential to prepare your animals for vaccination and support their immune response. You should provide a balanced diet that includes adequate levels of protein, vitamins, and minerals, especially those that boost immunity like vitamin E and selenium. Fresh, clean water must always be available to keep animals hydrated and facilitate nutrient absorption. Avoid sudden dietary changes before vaccination, as they can stress animals and weaken their immune systems. If animals are underweight or show signs of nutritional deficiencies, address these issues ahead of time. Proper nutrition helps animals recover quickly if they experience mild side effects from vaccines and guarantees their bodies are primed to develop effective immunity. Consistent, quality feeding is a key step in effective vaccination preparation. Recognizing relationships and understanding how to strengthen them can also contribute to a healthier environment for your livestock.
Schedule Vaccination Timing
Scheduling the right time for vaccination is crucial to maximize its effectiveness and minimize stress for your animals. You should plan vaccinations during calm periods when animals are healthy and not under stress from extreme weather or recent transport. Avoid vaccinating right before or after stressful events, like weaning or moving. Ideally, schedule vaccinations a few weeks before winter sets in so animals develop immunity before exposure to cold, damp conditions. Check your veterinarian’s recommendations for the ideal timing based on the vaccine type and local disease risks. Consistency is key, so stick to a regular schedule to ensure all animals are protected. Proper timing helps your livestock build immunity early, safeguarding them during the harsher winter months. Incorporating preventive care practices can further enhance your animals’ resilience against winter health issues.
Proper Vaccination Techniques and Handling
Proper vaccination techniques and handling are essential to guarantee the safety and effectiveness of livestock immunizations. To do this, you should follow these steps:
- Use clean and sterile equipment to prevent infections and ensure accurate dosing.
- Handle animals gently to reduce stress, which can interfere with vaccine response.
- Administer vaccines correctly—whether via injection, oral, or nasal route—by following manufacturer instructions precisely.
- Observe proper restraint to keep both you and the animal safe during the process.
- Proper handling also involves understanding the benefits of vaccination, such as improved herd health and disease prevention, which are crucial during seasonal changes.
Monitoring and Post-Vaccination Care

After administering vaccines, your focus should shift to closely monitoring the animals for any immediate reactions and signs of adverse effects. Watch for swelling, redness, or pain at the injection site, as well as more serious symptoms like difficulty breathing, fever, or lethargy. Keep a close eye on their behavior—if they seem distressed or unusually quiet, take note. Make sure they have access to clean water and a comfortable environment to support recovery. Record any reactions to track patterns or identify potential issues. If you notice severe or prolonged symptoms, contact your veterinarian promptly. Regular vacuuming of the bedding and living areas can help reduce dust and allergens that may exacerbate health issues. Consistent monitoring helps catch problems early and ensures your livestock recover quickly, maintaining their health and productivity as winter approaches.
Addressing Challenges and Common Concerns

While vaccination is essential for protecting your livestock, you may encounter challenges such as vaccine hesitancy among workers, logistical hurdles, or concerns about side effects. To address these issues:
- Educate your team about vaccine safety and benefits to reduce hesitancy.
- Plan logistics carefully, including storage and scheduling, to ensure smooth administration.
- Communicate transparently about possible side effects, emphasizing their rarity and management.
- Seek expert advice if uncertainties arise, especially regarding vaccine types or timing.
- Ensuring color accuracy in vaccine storage and handling can help preserve vaccine efficacy and safety.
Record-Keeping and Tracking Vaccination Status

Keeping accurate records of your livestock’s vaccination status is essential to guarantee effective disease prevention and timely administration. You should maintain a detailed log that includes dates of vaccinations, vaccine types, batch numbers, and expiration dates. Using digital tools or paper records makes tracking easier and helps prevent missed doses. Regularly update your records immediately after administering vaccines to ensure accuracy. This practice allows you to quickly verify which animals need boosters and identify any gaps in your herd’s vaccination schedule. Proper record-keeping also simplifies communication with veterinarians and complies with health regulations. By staying organized, you reduce the risk of vaccine errors, improve herd health management, and ensure your livestock are protected ahead of winter’s challenges.
Planning for Future Vaccination and Herd Health Maintenance

To keep your herd healthy, you need to plan vaccination timing carefully and stay on schedule. Consistently maintaining herd immunity requires strategic planning and regular updates. By staying proactive, you guarantee your livestock remain protected against preventable diseases.
Scheduling Vaccination Timing
Planning the timing of livestock vaccinations is essential to maintain herd health and prevent disease outbreaks. Proper scheduling ensures animals develop immunity before exposure peaks. To organize effectively, consider these steps:
- Assess disease risks based on your region and herd history.
- Identify ideal vaccination windows to allow immunity development before potential exposure.
- Coordinate with vaccination protocols recommended by veterinarians.
- Schedule follow-up boosters to sustain immunity over time.
Maintaining Herd Immunity
After scheduling initial vaccinations, it’s important to look ahead and guarantee herd immunity remains strong over time. To do this, you should keep track of vaccination schedules and ensure booster shots are administered on time. Regular health assessments help identify any animals that may not have developed full immunity, so you can address gaps promptly. Maintaining good nutrition and hygiene also supports an effective immune response. Stay alert for signs of disease outbreaks or waning immunity, and be prepared to update your vaccination plan as needed. Consistent monitoring and timely boosters ensure your herd stays protected, especially during winter when animals are more vulnerable. By planning ahead, you maintain herd health and prevent future outbreaks.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should I Vaccinate My Livestock During Winter?
You should vaccinate your livestock according to your veterinarian’s recommendations, usually once or twice a year. During winter, it’s essential to keep up with scheduled vaccinations to prevent illness, especially when animals are housed indoors or in close quarters. Regular vaccinations help protect against common winter diseases. Always check your local guidelines and consult your vet for a tailored schedule based on your livestock’s specific needs and regional risks.
Are There Specific Vaccines for Different Types of Livestock?
Yes, there are specific vaccines for different types of livestock. You should choose vaccines tailored to your animals, like cattle, sheep, or goats, because each species faces different health risks. Consult your veterinarian to identify the appropriate vaccines for your livestock. Regular vaccination helps protect against common diseases, ensuring your animals stay healthy during winter and beyond. Always follow the recommended schedules for each vaccine type.
What Are Signs of Adverse Reactions Post-Vaccination?
Oh, the thrill of post-vaccination excitement! You’ll notice swelling or redness at the injection site, maybe some mild fever or lethargy. In rare cases, watch for allergic reactions like difficulty breathing, hives, or sudden swelling. If your livestock suddenly acts like they’ve lost their mind or can’t stand, it’s time to act fast. Remember, quick intervention can turn a minor mishap into a story of veterinary heroism.
Can Vaccination Be Combined With Other Health Treatments?
Yes, you can combine vaccination with other health treatments, but you should always consult your veterinarian first. Some treatments might interfere with vaccine effectiveness or cause adverse reactions. It’s crucial to schedule treatments carefully, making sure they don’t stress the animals or compromise their immune systems. Always follow professional advice to ensure the safety and health of your livestock, especially when combining multiple health interventions.
How Do I Choose a Reputable Vaccine Supplier or Provider?
You should look for a reputable vaccine supplier by checking their certifications, reviews, and track record. Ask for references from other farmers and verify that they comply with local regulations. Make certain they provide clear product information, proper storage, and handling instructions. It’s also wise to consult your veterinarian for recommendations, as they can guide you toward trusted providers and help you select the best vaccines for your livestock’s needs.
Conclusion
Remember, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. By vaccinating your livestock ahead of winter, you’re safeguarding their health and your livelihood. Stay proactive with your vaccination schedule, choose the right vaccines, and keep detailed records. With proper planning and care, you can face winter confidently, knowing your herd is protected. Don’t wait for trouble to knock—take action now to ensure a healthy, thriving herd all season long.










