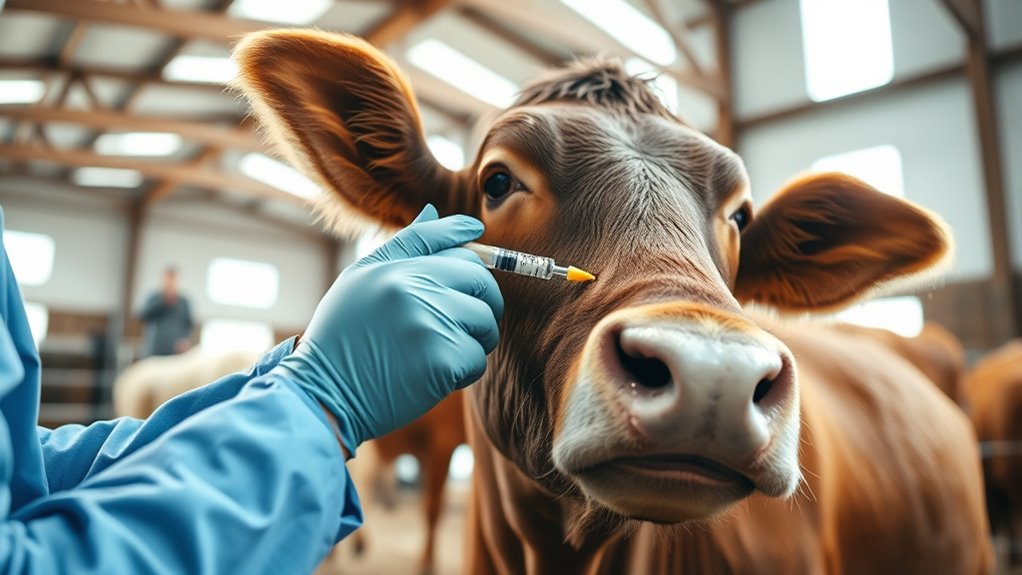
To create an effective pre-winter vaccination calendar for cattle, plan to administer core vaccines like clostridial, bovine herpesvirus, BVD, and leptospirosis about 3-4 weeks before cold weather begins. Schedule boosters as needed and prioritize proper storage, sterile handling, and record-keeping to guarantee vaccine potency and herd immunity. Monitoring responses helps confirm protection, and adjusting your plan based on herd conditions enhances effectiveness. Keep learning more to fully protect your cattle during winter.
Key Takeaways
- Schedule initial vaccinations 3-4 weeks before cold weather to ensure optimal immunity.
- Include vaccines for diseases like bovine herpesvirus, parainfluenza, and clostridial illnesses in your calendar.
- Plan booster shots according to vaccine requirements and herd-specific health assessments.
- Maintain proper vaccine storage and handling to ensure potency and effectiveness.
- Record vaccination dates and monitor responses to confirm herd immunity before winter.
Understanding the Importance of Pre-Winter Vaccinations
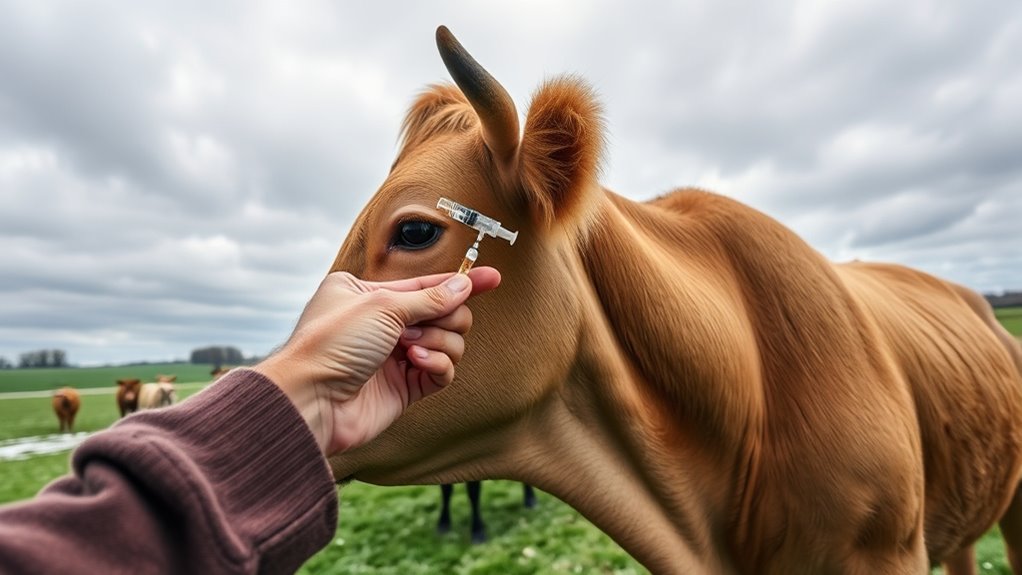

As winter approaches, it’s crucial to recognize why pre-winter vaccinations are essential for your health. Proper vaccine storage ensures the potency of each shot, preventing spoilage and guaranteeing your cattle receive effective protection. Vaccinating before winter helps build herd immunity, reducing the risk of disease outbreaks when animals are most vulnerable. When your herd is vaccinated early, it creates a protective barrier, preventing the spread of illnesses that thrive in cold, indoor conditions. Skipping or delaying vaccines can leave your cattle exposed to preventable diseases, leading to health issues and economic losses. Additionally, understanding the importance of floating on water can help you incorporate hydrotherapy techniques to support herd recovery and wellness. By prioritizing timely vaccinations and maintaining correct vaccine storage, you strengthen your herd’s resilience and promote overall herd health during the critical winter months. Ensuring proper vaccine storage and handling is vital to maintaining vaccine efficacy and safeguarding your herd’s health. Proper vaccine handling techniques can further maximize effectiveness and ensure your cattle are well-protected during the winter season. Moreover, staying informed about disease prevention strategies can further enhance your herd’s immunity and reduce the risk of outbreaks. Incorporating essential oils for immune support can also be beneficial in naturally boosting your herd’s defenses against common winter ailments.
Key Diseases to Protect Cattle Against Before Winter

Preparing your cattle for winter means identifying and protecting against key diseases that thrive in colder, indoor conditions. Respiratory diseases like Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) pose a significant risk, so vaccinating against pathogens such as bovine herpesvirus and parainfluenza boosts vaccine efficacy. Proper vaccination supports herd immunity, reducing disease spread within your group. Clostridial diseases, including blackleg and malignant edema, also threaten cattle during winter’s stress, making timely vaccination vital. Additionally, consider vaccines for infectious diseases like leptospirosis and bovine viral diarrhea (BVD), which can cause severe health issues. Strengthening immunity before winter guarantees your herd is better protected, decreases illness outbreaks, and maintains overall herd health. Resources and Tools can help you identify the most effective vaccination strategies to protect your herd. Implementing vaccination protocols based on current research enhances disease prevention efforts during this critical period.
Timing Your Vaccination Schedule for Optimal Coverage
Timing your vaccination schedule correctly guarantees your cattle build strong immunity before winter’s challenges. Plan vaccinations at least 3-4 weeks prior to cold weather to maximize herd immunity. Proper vaccine storage is essential to guarantee effectiveness; keep vaccines refrigerated and follow manufacturer guidelines. Schedule booster shots based on the vaccine’s timing requirements, avoiding gaps that could leave cattle vulnerable. Regularly reviewing vaccination protocols ensures your program remains effective and up-to-date. Here’s a visual to help you organize:
| Week | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Administer initial vaccine |
| 2 | Monitor cattle and store vaccines properly |
| 3-4 | Provide booster if needed |
| 5 | Confirm herd immunity levels |
| 6 | Prepare for winter challenges |
Ensuring the correct timing of vaccinations helps reduce the risk of disease outbreaks and herd immunity is strengthened through proper scheduling. Additionally, considering the efficiency of your vaccination program can further enhance protection against winter illnesses. Incorporating proper handling techniques minimizes vaccine wastage and maximizes immune response, ensuring your herd remains healthy throughout the season. Proper vaccine administration techniques are vital for achieving optimal results and maintaining herd health.
Selecting the Right Vaccines for Winter Preparedness
Choosing the right vaccines is essential to make certain your cattle are well-protected against winter hazards. Start by selecting vaccines that target diseases common during colder months, such as respiratory illnesses and clostridial diseases. Proper vaccine storage is critical; keep vaccines refrigerated and follow manufacturer instructions to maintain potency. When selecting vaccines, consider your herd’s current health status and vaccination history to ensure maximum herd immunity. Vaccines that promote strong herd immunity help prevent outbreaks, especially when cattle are housed closely together or stressed by cold weather. Always verify vaccine expiration dates and storage conditions before use. Additionally, understanding heat pump technology and its benefits can assist in creating optimal indoor environments for cattle during winter. Maintaining good biosecurity practices can further reduce disease transmission risks during the winter months. Implementing proper sanitation protocols can also help minimize pathogen spread within the herd. Using vaccination schedules tailored to seasonal risks can enhance overall herd health and resilience during winter. Ensuring proper vaccine administration techniques can improve their efficacy and provide better protection to your herd. By choosing appropriate vaccines and maintaining proper storage, you’ll enhance your herd’s resilience, reducing winter-related health risks and ensuring a healthier, more productive season.
Administering Boosters: Best Practices and Techniques
After selecting the right vaccines for winter protection, administering boosters correctly guarantees your herd maintains strong immunity. Proper technique guarantees the vaccine’s effectiveness and preserves herd immunity. First, always check vaccine storage; vaccines must stay within recommended temperature ranges to prevent degradation. Second, prepare your equipment—use sterile needles and syringes to avoid contamination. Third, administer the booster at the correct site and dose, following manufacturer instructions. Be sure to record each vaccination for future reference. Consistent practices reduce stress on cattle and improve vaccine uptake. Proper storage and handling minimize waste and ensure the vaccine’s potency. Additionally, being aware of vaccine ingredients and avoiding certain substances can further enhance vaccine safety. Utilizing effective administration techniques can also improve the immune response and overall herd health. Regular training on administration procedures helps ensure that staff are confident and competent, leading to better outcomes. Staying informed about home security systems and their benefits can help implement safety measures on farms or ranches. Incorporating proper sanitation practices can further reduce the risk of infection and improve vaccine effectiveness. When done correctly, your herd develops a resilient immune response, providing reliable winter protection.
Recognizing Signs of Vaccine Response in Cattle
When monitoring cattle after vaccination, look for noticeable behavioral changes like increased alertness or reduced activity. Keep an eye on physical signs such as swelling or mild fever, which indicate a response. Remember, it’s important to track these signs during the appropriate monitoring period to guarantee your cattle are responding properly. Additionally, understanding the vaccine response timeline can help you better interpret these signs and determine when to seek veterinary advice.
Observable Behavioral Changes
Recognizing observable behavioral changes is essential for evaluating how cattle respond to vaccinations. By paying close attention to behavioral observation, you can identify subtle signs of the vaccine’s effect. Look for shifts in social dynamics, such as:
- Decreased activity levels or lethargy
- Changes in grazing or feeding behavior
- Increased restlessness or agitation
These behaviors may indicate the animal’s immune response or mild discomfort. Social dynamics can also shift if cattle become more withdrawn or overly clingy with herd mates. Monitoring these signs helps you gauge vaccine reactions without invasive measures. Remember, each animal may respond differently, so consistent observation over time is key. Being attentive to these behavioral cues ensures you can address any issues promptly and support your herd’s well-being.
Physical Health Indicators
Monitoring physical health indicators provides tangible signs of how cattle respond to vaccination. Watch for changes in appetite, coat condition, and activity levels, as these reflect their overall health. Cattle with strong genetic resilience often show quicker recovery and fewer side effects, while those with weaker resilience may exhibit mild swelling or slight fever. Environmental factors, such as weather or herd density, can influence these responses, making it essential to *evaluate* external conditions when *examining* health. Look for localized swelling or soreness at injection sites, which typically indicate an effective immune response. Maintaining consistent observation of these indicators helps you determine if the vaccine is working and whether cattle are adapting well to the immunization process.
Monitoring Duration Period
The duration of the monitoring period is essential for accurately evaluating how cattle respond to vaccination. Proper monitoring helps you assess vaccine efficacy and identify signs of a successful immune response. During this time, focus on recognizing these key indicators:
- Look for a reduction in disease symptoms or severity.
- Observe increased resilience against common pathogens.
- Note any adverse reactions or persistent side effects.
This monitoring duration allows you to determine if the vaccine has effectively boosted immunity. Consistent observation ensures you catch early signs of a strong response or potential issues. By understanding these signs, you can make informed decisions about future vaccinations and overall herd health, maximizing the benefits of your pre-winter booster program.
Managing Vaccination Records for Effective Monitoring

Keeping accurate vaccination records is essential for ensuring individuals stay protected and for tracking overall public health progress. Proper record management helps you monitor vaccination schedules, identify gaps, and ensure timely boosters. To do this effectively, you need a reliable system to document each vaccination, including date, vaccine type, and batch number. Additionally, proper vaccine storage is crucial; storing vaccines correctly preserves their effectiveness and prevents wastage. Maintain organized records, whether digitally or on paper, to easily access and update information. Regularly review your records to confirm compliance with the vaccination calendar and identify any missed doses. Accurate record management ensures you can quickly respond to outbreaks, verify vaccination status, and improve overall herd health management.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Scheduling Vaccinations

One common mistake is not paying attention to the recommended vaccine timing, which can reduce its effectiveness. Ignoring proper dosages or missing follow-up shots can leave you unprotected or require additional appointments. To stay on track, make sure you understand the schedule and follow it carefully.
Overlooking Vaccine Timing
Failing to pay close attention to vaccine timing can lead to missed opportunities for ideal immunity. If you don’t time vaccinations correctly, you risk gaps in herd immunity and compromised protection. To avoid this, consider these points:
- Schedule vaccines well before anticipated exposure, ensuring the immune response develops in time.
- Maintain proper vaccine storage; improper storage can reduce effectiveness, wasting resources.
- Monitor your herd’s vaccination schedule and follow recommended intervals, preventing missed doses.
Timing is vital for maximizing vaccine efficacy and ensuring cattle are protected when they’re most vulnerable. Overlooking these details can undermine herd immunity and leave your cattle at risk. Stay vigilant about vaccination timing to secure optimal health and productivity.
Ignoring Proper Dosage
Ignoring proper vaccine dosage can considerably weaken your herd’s immunity and reduce the effectiveness of the vaccination program. If you don’t follow recommended dosage accuracy, you risk underdosing or overdosing, which can compromise protection. Proper vaccine storage is essential; vaccines stored improperly may lose potency, leading to ineffective results even if dosage instructions are correct. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines for storage conditions and ensure vaccines are kept at the right temperature. When administering vaccines, measure doses carefully, avoiding shortcuts or guesswork. Using incorrect dosages not only diminishes herd immunity but can also cause adverse reactions. Protect your cattle by adhering strictly to dosage instructions and maintaining proper vaccine storage practices. This attention to detail ensures a strong, healthy herd ready for winter.
Skipping Follow-up Shots
Proper vaccine dosages are essential, but even with correct administration, missing follow-up shots can leave your herd vulnerable. Skipping these critical doses undermines herd immunity and risks disease outbreaks. To avoid this mistake:
- Ensure proper vaccine storage to maintain effectiveness and prevent spoilage.
- Follow the recommended schedule precisely, including booster shots, to reinforce immunity.
- Keep detailed records to track missed doses and upcoming vaccinations.
Missing follow-up shots weakens the protection your herd needs during winter and can lead to preventable illnesses. Consistent scheduling and proper vaccine storage are key to maintaining immunity and safeguarding your cattle. Don’t compromise on follow-up vaccinations—they’re indispensable for a healthy, resilient herd.
Adjusting Your Plan for Different Herd Conditions
Adjusting your vaccination plan is essential because herd conditions can vary widely and impact how you should approach immunizations. If your herd has been selected through genetic selection for disease resistance, you might reduce certain vaccines or extend intervals. Conversely, if pasture management results in dense grazing areas with high disease exposure, you’ll need to prioritize vaccines that protect against specific pathogens. Regularly assess herd health, genetics, and grazing practices to determine which vaccinations are most effective. Keep in mind that different herd conditions might require tailored schedules to optimize immunity and prevent outbreaks. Staying flexible and informed about your herd’s unique needs helps ensure your vaccination strategy remains effective and cost-efficient throughout the winter months.
Preparing for Unexpected Health Challenges During Winter

Winter can bring sudden health challenges that catch even well-prepared herds off guard. To stay ahead, focus on three key steps:
- Make certain proper vaccine storage—keep vaccines at the right temperature to maintain effectiveness, especially during cold months.
- Strengthen herd immunity by administering pre-winter boosters, reducing susceptibility to common winter illnesses.
- Monitor herd health closely, watching for signs of illness and acting quickly if issues arise.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Determine the Best Vaccination Timing for My Specific Herd?
To determine the best vaccination timing for your herd, consider their disease risk and herd age. You need to assess which illnesses are more prevalent in your area and when your cattle are most vulnerable. Younger animals may require earlier vaccination, while older ones might need boosters at specific intervals. Consult your veterinarian and review local disease reports to develop a tailored schedule that offers ideal protection for your herd.
What Are the Costs Associated With Winter Vaccination Programs?
You need to contemplate costs like vaccine storage and maintaining the cold chain, which are vital for effectiveness. Proper storage requires refrigeration, adding to your expenses. If cold chain management isn’t maintained, vaccines may become ineffective, leading to wasted money. Additionally, factor in labor costs for administering vaccines and potential veterinary fees. These combined costs guarantee your winter vaccination program is both effective and economically sustainable.
Can Vaccination Schedules Be Adjusted for Organic or Natural Herds?
Imagine your herd as a garden, thriving with natural harmony. For a natural herd following organic practices, you can adapt vaccination schedules to align with these values, focusing on minimal intervention. Instead of routine shots, consider targeted vaccinations that respect your herd’s natural immunity. By customizing your plan, you ensure your cattle stay healthy while honoring organic principles, creating a balanced, resilient herd that grows stronger naturally.
How Do Climate Variations Affect Vaccine Efficacy and Timing?
Climate impact plays a vital role in vaccine timing and efficacy. You need to take into account how temperature fluctuations and humidity affect vaccine stability, as extreme weather can degrade vaccines or reduce their effectiveness. By monitoring climate conditions, you can better time your cattle vaccinations to guarantee maximum immune response. Adjusting schedules based on climate variations helps protect your herd and maintains vaccine potency, especially during unpredictable seasonal changes.
What Are the Legal Requirements or Recommended Protocols for Cattle Vaccination?
You need to follow legal compliance and guarantee your vaccines have proper approvals before use. Check with local authorities or veterinary guidelines for specific protocols, including mandatory vaccinations and record-keeping. Always use vaccines approved by relevant agencies to guarantee safety and efficacy. Adhering to recommended protocols helps protect your cattle, avoid legal issues, and maintain a healthy herd. Stay informed about any updates or changes in vaccination regulations in your region.
Conclusion
By following a well-planned vaccination calendar, you can confidently safeguard your cattle from winter diseases. Think of it like building a sturdy shield—each booster reinforces your herd’s defenses. Just as a chain is only as strong as its weakest link, neglecting timely vaccines can leave gaps in protection. Stay proactive, keep records, and adjust your plan as needed. Your vigilance now ensures healthy, resilient cattle all winter long.










